
Until a few years ago, people probably thought Lyme disease was something that happened when you had too many “bottomless cup” margaritas at the local watering hole. But Lyme disease is no laughing matter. Educating yourself on Lyme disease facts and myths can be the difference between you continuing to enjoy a life full of the outdoors, and battling a chronic illness.
According to the Center for Disease Control, Lyme disease is the fastest growing and most prevalent bug-borne disease in the nation with more than 300,000 people diagnosed each year. Many experts estimate less than 25% of new cases are being accurately diagnosed, and only a fraction of chronic Lyme cases are positively identified.
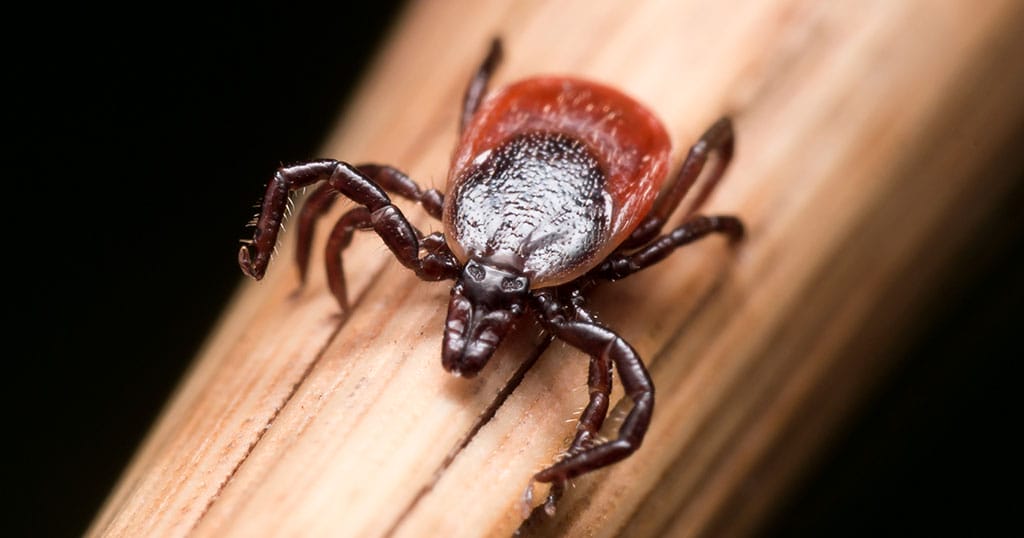
Lyme is one of the most misunderstood, misdiagnosed and, unfortunately, mistreated diseases in the U.S. It is caused by a bizarre organism called Borrelia burgdorferi. Borrelia is a corkscrew-shaped bacterium referred to as a spirochete. Because of its unique shape and properties, this bacterium can bore itself into muscles, bones and even nervous system tissues and wreak havoc on its host (you and me).
Lyme is often called “The Great Imitator” because its symptoms mimic many other diseases. It can affect any organ of the body, including the brain and nervous system, muscles, joints and heart. Patients with Lyme disease are frequently misdiagnosed with chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia, multiple sclerosis, crippling arthritis and various psychiatric and mental illnesses, including severe depression.
I spent the last 20 years of my life experiencing the long list of Lyme symptoms. I was misdiagnosed dozens of times and had two “falsely” negative tests that delayed my diagnosis for nearly 15 years. Educating yourself on Lyme disease facts can prevent you from ending up in a situation like mine.
Most people get Lyme from the bite of the nymphal, or immature, form of the tick. Nymphs are about the size of a poppy seed. Because they are so tiny and their bite is painless, many people don’t even realize they have been bitten. Once attached, an undisturbed tick may feed for several days. The longer it stays attached, the more likely it will transmit Lyme and other pathogens into your bloodstream.
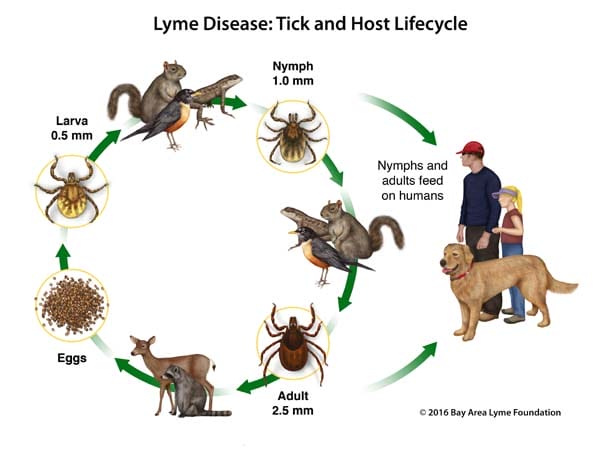
9 Lyme Disease Facts:
- According to the CDC, Lyme disease is the fastest growing vector-borne, infectious disease in the U.S.
- The number of cases reported annually has increased nearly 25-fold since National Surveillance began in 1982.
- There are five subspecies of Borrelia burgdorferi, over 100 strains in the U.S., and 300 strains worldwide.
- CDC estimated cases: 25,000 cases per week, 5,770 cases per day, 822 cases per hour (many experts believe less than 10% of Lyme cases are reported)
- There are no tests available to prove that the organism is eradicated or the patient is cured.
- Fewer than 50% or patients with Lyme disease recall a tick bite.
- Forty percent of Lyme patients end up with long-term health problems.
- Fewer than 50% of patients with Lyme disease recall a rash.
- Up to 70% of ticks in Lyme-endemic areas are infected.
Find more Lyme Disease facts HERE.
3 Lyme Disease Myths:
MYTH: Everyone with Lyme disease gets a telltale bull’s-eye rash.
Actually, many never develop a skin rash and those that do may not get a bull’s-eye rash. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimate that only 70% develop a skin rash (erythema migrans), but this can vary by region. For example, a 2010 study showed that in the state of Maine only 43% of Lyme patients exhibited this particular type of rash. There are a range of symptoms and it is critical that you are alert to all of them.
MYTH: Antibiotics cure everyone.
While an estimated 329,000 people are diagnosed with Lyme disease each year, statistics show that as many as 20% of patients continue to exhibit symptoms even after antibiotic treatment. While there is controversy about the cause of this symptom persistence (e.g., residual bacteria or auto-immune response), for these patients, the suffering continues. As many as a million Americans are estimated to be suffering with this condition, referred to as post-treatment Lyme disease (PTLD).
MYTH: If the test is negative, you don’t have Lyme.
Not so fast … The current “gold standard” diagnostic for Lyme disease is a two-tiered blood test requiring a positive ELISA result. The ELISA measures infection-fighting or memory antibodies against Borrelia burgdorferi, and it misses up to 60% of acute cases of Lyme when antibodies may not be high enough to detect.
Myths courtesy of Bay Area Lyme Foundation
Think you may have Lyme disease? Check your symptoms HERE.
Written by Scott Vance, Union Sportsmen’s Alliance – CEO







